Can you answer these three questions?
- Off-site
- Are your backups secured away from your premises? What happens if your primary site is compromised and your live system data is lost together with your backups?
- Version control
- How may distinct sets of backups do you keep? Do you have a history of backups? Are they easily identifiable? Are your data images complete, usable and unique?
- Verify
- Are you sure that the backup you made actually contains the data you think it does? Is it current?
Why use MrBackup? Use this checklist to compare other products with MrBackup.

 Ease of Use
Ease of Use
Automated or One-Touch backups. Click it, or leave it for the scheduler. Once configured, the system can make user initiated or user-independent, scheduled backups. Anytime, unlimited uploads.
 Daily, Weekly, Monthly
Daily, Weekly, Monthly
Version Control made easy with multiple snapshot backups: at least eight (8) complete sets of data stored, allowing access to different versions of the same data. Each backup is a unique, complete set of the backed up data. Data upload verified to ensure the full backup is received and stored on the server. Make a backup every day!

Windows
Windows 10 Designed for Microsoft Windows, scalable on a variety of operating systems, from standalone PCs, to dedicated servers. Runs on any Windows XP+ OS, no special servers or hardware required. Windows Server compatible, but not required. Works on Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7 and Windows 8, Windows 8.1 and Windows 10. Also works on Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2012 R2.
 Designed for Small Business
Designed for Small Business
Who should use MrBackup? Any small business – doctors, lawyers, engineering firms, retailers, estate agents. Any SME with valuable data should make sure it can survive in business suffering loss to its data. MrBackup provides this service at a very favorable cost/benefit ratio!
 Email Reports
Email Reports
With every upload an automated email message is sent confirming the current upload, verbosely reporting all data currently stored on the server. Keeps all role players who should be up to date with the status of the backup, in the loop!
 SQL Friendly
SQL Friendly
SQLBackupandFTP compatible. MrBackup relies on the Command Line interface to trigger the creation of the on-disk file, which is then rapidly backed up off-site.
 No disruption
No disruption
Non-intrusive background backup. Network users can continue using their software while the backup is in progress.
 Off-site
Off-site
Data stored at a remote, secure, off-site location, far from the troubles of the world.
 Customization
Customization
Data is typically located on a central server/master computer and shared by LAN users. Core data is identified and this critical central data source is backed up. MS Access, SQL, PDFs, DBFs, .ODB, .doc / .docx, .xls / .xlsx etc.
 Speed
Speed
Rapid upload – at least 15 MB per minute or better. Average upload 5-12 minutes. Uploads speeds are dependent on the underlying broadband solution used. 512 MB on-disk data backed up over 3G in less than 40 minutes.
 Safe and Secure
Safe and Secure
Secure Remote Data Storage: Two high level data encryption systems and fully compliant 1024 bit SSH-2 digital certificates are used.
User Level Password encryption in the form of AES passwords can also be used.
AES Security implementation is used by NASA, the CIA and all major banks.
 Reliable
Reliable
100% successful data restore in disaster conditions.
 Cost Effective
Cost Effective
MrBackup’s Core Data Model ensures that critical data that needs protection is properly protected. MrBackup’s unique combination of customization, ease of use, speed and reliability combine to create exceptional client cost/benefit ratios.
MrBackup’s many small business customer’s can also opt to use the auto System Shutdown at the end of the day. Simply leave the PC on, and after the backup is complete, the system will be safely shutdown. This also works on Windows 8 and Windows 8.1!
From the Tech Republic website: 10 things to look for in an offsite backup provider
Thank you for using www.mrbackup.net
In this section we discuss Frequently Asked Questions regarding the MrBackup service and Data Backup in general.
Glossary
Disaster Recovery, is the process, policies and procedures related to preparing for recovery or continuation of technology infrastructure critical to an organization after a natural or human-induced disaster. For a discussion of Disaster Recovery, please visit the Wikipedia entry for ‘Disaster Recovery.’ From the Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Disaster_recovery
Off-site data protection, or vaulting, is the strategy of sending critical data out of the main location (off the main site) as part of a disaster recovery plan. From the Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/offsite_data_protection
Recovery Potential defines the prospects of successful disaster recovery. Recovery Time Objectives indicate how long a system can be down before the disaster leads to business failure, and Recovery Point Objectives indicate how much data can reasonable be lost by a system before such loss leads to business failure. For an extensive discussion of the importance of computer data back up and the role of such backups in disaster recovery, please visit the Wikipedia entry for ‘Backup’: From the Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Backup
RAID, acronym for Redundant Array of Independent Disks (originally Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks), is a storage technology that provides increased reliability and functions through redundancy. From the Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RAID
Are we making backups of the wrong data?
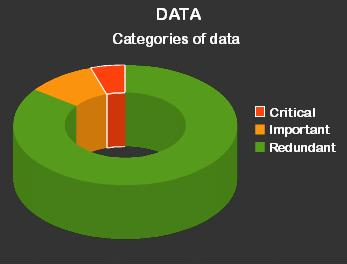 MrBackup is based on a ‘core data model’ which assumes that only mission critical/business critical data requires protection. It is assumed that on any given computer.
MrBackup is based on a ‘core data model’ which assumes that only mission critical/business critical data requires protection. It is assumed that on any given computer.
|
What kind of data can I backup?
MrBackup uses an open ended data source approach. This means that any data that exists on a Windows OS based computer can be stored. It does not matter if your data consists of images such as photos of friends and family, important MS Word documents, spreadsheets, email or important accounting records, or sophisticated SQL systems, MrBackup is designed, and capable to store any data. MrBackup guarantees a 0% risk of fuzzy backup! If its on a computer, MrBackup can store it!
How does the version control work?
MrBackup has a unique version control mechanism to ensure that multiple, complete data sets are backed up uniquely and separately from each other. This means that if any single backup turns out to be damaged, incomplete or unusable, it is still possible to fall back on earlier complete data sets of the same backed up data. The main advantage to this system is that in the event that the most recent backup can not be used, several previous versions still exist.
MrBackup guarantees at least eight (8) complete unique data sets. This means that if the data becomes corrupt due to software failure, user error, real-time data corruption or virus attack, MrBackup will still have several chronological complete unique data sets which may be restored. This is the main difference between a true backup and a data security system such as RAID.
Why off-site data protection?
MrBackup offers the ideal solution to enterprises requiring fast, reliable, hot, off-site data storage. Our solution requires broadband Internet connectivity for the duration of the backup process, but does not involve any form of mirroring and the backup is only available on demand, so can not be described as being ‘on-line.’ As such our multiple version data storage model allows for the rapid restoration of any unique version of client data from our electronic vault. Secure remote data storage, electronic vaulting, is a critical aspect of increased disaster recovery potential.
Backup or Archive?
The literature on electronic data backup and archiving can be confusing. The underlying assumption is that data changes continuously and that current ‘live’ data will not look the same as older historical data. Backup is used for short-term operational requirements; Archives are used for non-operational long term reasons. Multiple backups are always advised. Our simple definitions are as follows:
backup (noun) a copy of current data, with a short life cycle, primarily for use in the recovery and restoration of the original system in the event of data loss, intended to restore data with the express purpose of restoring a live system from data loss; verb – the act of backing up data
archive (noun) an older copy (backup) of data retained for an extended period of time, primarily used in restoring a system to an historical Point-in-Time for analytical purposes or statutory compliance, not suitable to restore a live system to operational efficiency; verb – the act of archiving data
What about Cloud Computing?
Cloud Computing appears to be an easy solution to most backup needs. However, Cloud Computing, or putting your data ‘in the cloud’, such as through remote hosting or Terminal Services products, could create a false sense of security. The first problem is that not all computer data exists as ‘user accessible files on disk’. Applications need to designed specifically with cloud computing in mind. Applications that use advanced data management systems, such as SQL, store data in on-disk files. Simply copying a SQL folder to a different location will not guarantee that it works in the event of disaster recovery.
Cloud Computing is not a backup system and a lot of care needs to be taken when evaluating the different providers. Problems that can occur include:
• Denial of service, caused by terrorism and natural disasters.
• Hacking, the classic example is certainly the successful hacking of Sony’s PS3 network .
• Bandwidth restrictions, and
• Partial or incomplete backups
To RAID or Not to RAID?
RAID is not a true data backup system. RAID is a data security technology designed primarily to protect against physical hardware failure or loss of access to data due to hardware or electrical failure. RAID and traditional data backups are not competing technologies, but supplement each other. Both RAID and traditional data backups form part of a data security strategy. Both are important, but not mutually exclusive. RAID is designed to provide maximum data security against physical failure and minimize system downtime. RAID in itself can however not restore data to a specific Point in Time. Traditional data backups could restore data to a required specific Point in Time. In the event of non-physical failure RAID offers no solution. With limited resources, RAID should take second place to traditional backups. Please see the table below which compares RAID to traditional data backup.
| Data Risk | Traditional Backup | Raid | Cloud |
| Catastrophic Data Loss | Okay | FAIL | Okay |
| Fire, Flood, Theft, Terrorism | Okay | FAIL | Okay |
| Physical Disk Failure | Okay | Okay | Okay |
| Denial of Service (DoS) attack Bandwidth restrictions |
Okay | Okay | FAIL |
| Intentional malicious data corruption due to virus or hacker attacks |
Okay | FAIL | FAIL |
| Non-Intentional data corruption due to human error or system malfunction |
Okay | FAIL | FAIL |


[…] Check List & FAQ […]